koa 框架一直都保持着简洁性, 它只对 node 的 HTTP 模块进行了封装, 而在真正实际使用, 我们还需要更多地像路由这样的模块来构建我们的应用, 而 koa-router 是常用的 koa 的路由库. 这里通过解析 koa-router 的源码来达到深入学习的目的.
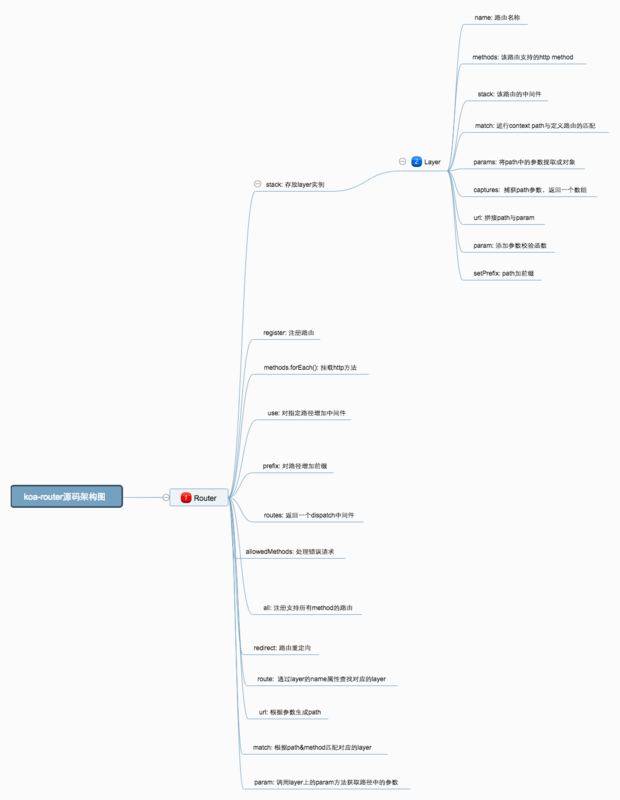
源码架构图
调用链路-routes()

HTTP请求调用流程

Usage
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
router.get('/', async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('index');
ctx.body = 'index';
});
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
app.listen(3000);Router
function Router(opts) {
if (!(this instanceof Router)) {
return new Router(opts);
}
this.opts = opts || {};
this.methods = this.opts.methods || [
'HEAD',
'OPTIONS',
'GET',
'PUT',
'PATCH',
'POST',
'DELETE'
];
// 存放router.param方法指定的参数的中间件
this.params = {};
// 存放layer实例
this.stack = [];
};Layer
function Layer(path, methods, middleware, opts) {
this.opts = opts || {};
this.name = this.opts.name || null;
this.methods = [];
// 存放path路径参数的一些属性,eg: /test/:str => { name: str, prefix: '/' ....}
this.paramNames = [];
// 存放该路由的中间件
this.stack = Array.isArray(middleware) ? middleware : [middleware];
methods.forEach(function(method) {
var l = this.methods.push(method.toUpperCase());
// 如果支持get请求,一并支持head请求
if (this.methods[l-1] === 'GET') {
this.methods.unshift('HEAD');
}
}, this);
// ensure middleware is a function
this.stack.forEach(function(fn) {
var type = (typeof fn);
if (type !== 'function') {
throw new Error(
methods.toString() + " `" + (this.opts.name || path) +"`: `middleware` "
+ "must be a function, not `" + type + "`"
);
}
}, this);
this.path = path;
// 将路由转为正则表达式
this.regexp = pathToRegExp(path, this.paramNames, this.opts);
debug('defined route %s %s', this.methods, this.opts.prefix + this.path);
};给Router实例挂载HTTP方法
/**
* Create `router.verb()` methods, where *verb* is one of the HTTP verbs such
* as `router.get()` or `router.post()`.
*
* Match URL patterns to callback functions or controller actions using `router.verb()`,
* where **verb** is one of the HTTP verbs such as `router.get()` or `router.post()`.
*
* Additionaly, `router.all()` can be used to match against all methods.
*
* ```javascript
* router
* .get('/', (ctx, next) => {
* ctx.body = 'Hello World!';
* })
* .post('/users', (ctx, next) => {
* // ...
* })
* .put('/users/:id', (ctx, next) => {
* // ...
* })
* .del('/users/:id', (ctx, next) => {
* // ...
* })
* .all('/users/:id', (ctx, next) => {
* // ...
* });
* ```
*
* When a route is matched, its path is available at `ctx._matchedRoute` and if named,
* the name is available at `ctx._matchedRouteName`
*
* Route paths will be translated to regular expressions using
* [path-to-regexp](https://github.com/pillarjs/path-to-regexp).
*
* Query strings will not be considered when matching requests.
*
* #### Named routes
*
* Routes can optionally have names. This allows generation of URLs and easy
* renaming of URLs during development.
*
* ```javascript
* router.get('user', '/users/:id', (ctx, next) => {
* // ...
* });
*
* router.url('user', 3);
* // => "/users/3"
* ```
*
* #### Multiple middleware
*
* Multiple middleware may be given:
*
* ```javascript
* router.get(
* '/users/:id',
* (ctx, next) => {
* return User.findOne(ctx.params.id).then(function(user) {
* ctx.user = user;
* next();
* });
* },
* ctx => {
* console.log(ctx.user);
* // => { id: 17, name: "Alex" }
* }
* );
* ```
*
* ### Nested routers
*
* Nesting routers is supported:
*
* ```javascript
* var forums = new Router();
* var posts = new Router();
*
* posts.get('/', (ctx, next) => {...});
* posts.get('/:pid', (ctx, next) => {...});
* forums.use('/forums/:fid/posts', posts.routes(), posts.allowedMethods());
*
* // responds to "/forums/123/posts" and "/forums/123/posts/123"
* app.use(forums.routes());
* ```
*
* #### Router prefixes
*
* Route paths can be prefixed at the router level:
*
* ```javascript
* var router = new Router({
* prefix: '/users'
* });
*
* router.get('/', ...); // responds to "/users"
* router.get('/:id', ...); // responds to "/users/:id"
* ```
*
* #### URL parameters
*
* Named route parameters are captured and added to `ctx.params`.
*
* ```javascript
* router.get('/:category/:title', (ctx, next) => {
* console.log(ctx.params);
* // => { category: 'programming', title: 'how-to-node' }
* });
* ```
*
* The [path-to-regexp](https://github.com/pillarjs/path-to-regexp) module is
* used to convert paths to regular expressions.
*
* @name get|put|post|patch|delete|del
* @memberof module:koa-router.prototype
* @param {String} path
* @param {Function=} middleware route middleware(s)
* @param {Function} callback route callback
* @returns {Router}
*/
var methods = require('methods');
methods.forEach(function (method) {
Router.prototype[method] = function (name, path, middleware) {
var middleware;
// 如果指定了路由name属性
if (typeof path === 'string' || path instanceof RegExp) {
middleware = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 2);
} else {
middleware = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
path = name;
name = null;
}
// 路由注册
this.register(path, [method], middleware, {
name: name
});
return this;
};
});Router.prototype.register
/**
* Create and register a route.
*
* @param {String} path Path string.
* @param {Array.<String>} methods Array of HTTP verbs.
* @param {Function} middleware Multiple middleware also accepted.
* @returns {Layer}
* @private
*/
Router.prototype.register = function (path, methods, middleware, opts) {
opts = opts || {};
var router = this;
// layer实例数组,初始为空数组
var stack = this.stack;
// support array of paths
if (Array.isArray(path)) {
// 如果是多路径,递归注册路由
path.forEach(function (p) {
router.register.call(router, p, methods, middleware, opts);
});
return this;
}
// create route
var route = new Layer(path, methods, middleware, {
end: opts.end === false ? opts.end : true,
name: opts.name,
sensitive: opts.sensitive || this.opts.sensitive || false,
strict: opts.strict || this.opts.strict || false,
prefix: opts.prefix || this.opts.prefix || "",
ignoreCaptures: opts.ignoreCaptures
});
// 设置前置路由
if (this.opts.prefix) {
route.setPrefix(this.opts.prefix);
}
// add parameter middleware
Object.keys(this.params).forEach(function (param) {
// 将router中this.params维护的参数中间件挂载到layer实例中
route.param(param, this.params[param]);
}, this);
// 所有layer实例存放在router的stack属性中
stack.push(route);
return route;
};Router.prototype.match
/**
* Match given `path` and return corresponding routes.
*
* @param {String} path
* @param {String} method
* @returns {Object.<path, pathAndMethod>} returns layers that matched path and
* path and method.
* @private
*/
Router.prototype.match = function (path, method) {
// layer实例组成的数组
var layers = this.stack;
var layer;
var matched = {
path: [],
pathAndMethod: [],
route: false
};
for (var len = layers.length, i = 0; i < len; i++) {
layer = layers[i];
debug('test %s %s', layer.path, layer.regexp);
// 1.匹配路由
if (layer.match(path)) {
matched.path.push(layer);
// 2.匹配http请求方法
if (layer.methods.length === 0 || ~layer.methods.indexOf(method)) {
matched.pathAndMethod.push(layer);
// 3.指定了http请求方法,判定为路由匹配成功
if (layer.methods.length) matched.route = true;
}
}
}
return matched;
};Router.prototype.routes
/**
* Returns router middleware which dispatches a route matching the request.
*
* @returns {Function}
*/
Router.prototype.routes = Router.prototype.middleware = function () {
var router = this;
var dispatch = function dispatch(ctx, next) {
debug('%s %s', ctx.method, ctx.path);
// 请求路由
var path = router.opts.routerPath || ctx.routerPath || ctx.path;
// 将注册路由和请求的路由进行匹配
var matched = router.match(path, ctx.method);
var layerChain, layer, i;
if (ctx.matched) {
ctx.matched.push.apply(ctx.matched, matched.path);
} else {
ctx.matched = matched.path;
}
ctx.router = router;
// route属性是三次匹配的结果,表示最终是否匹配成功
if (!matched.route) return next();
// 同时满足路由匹配和http请求方法的layer数组
var matchedLayers = matched.pathAndMethod
// 匹配多个路由时认为最后一个是匹配有效的路由
var mostSpecificLayer = matchedLayers[matchedLayers.length - 1]
ctx._matchedRoute = mostSpecificLayer.path;
if (mostSpecificLayer.name) {
ctx._matchedRouteName = mostSpecificLayer.name;
}
// 将匹配的路由reduce为一个数组
layerChain = matchedLayers.reduce(function(memo, layer) {
// 执行注册路由中间件之前,对context中的一些参数进行设置
memo.push(function(ctx, next) {
// :path/XXX 捕获的路径
ctx.captures = layer.captures(path, ctx.captures);
// 捕获的路径上的参数, { key: value }
ctx.params = layer.params(path, ctx.captures, ctx.params);
// 路由名称
ctx.routerName = layer.name;
return next();
});
// 返回路由中间件的数组
return memo.concat(layer.stack);
}, []);
// 处理为promise对象
return compose(layerChain)(ctx, next);
};
dispatch.router = this;
return dispatch;
};Router.prototype.allowedMethod
/**
* Returns separate middleware for responding to `OPTIONS` requests with
* an `Allow` header containing the allowed methods, as well as responding
* with `405 Method Not Allowed` and `501 Not Implemented` as appropriate.
*
* @example
*
* ```javascript
* var Koa = require('koa');
* var Router = require('koa-router');
*
* var app = new Koa();
* var router = new Router();
*
* app.use(router.routes());
* app.use(router.allowedMethods());
* ```
*
* **Example with [Boom](https://github.com/hapijs/boom)**
*
* ```javascript
* var Koa = require('koa');
* var Router = require('koa-router');
* var Boom = require('boom');
*
* var app = new Koa();
* var router = new Router();
*
* app.use(router.routes());
* app.use(router.allowedMethods({
* throw: true,
* notImplemented: () => new Boom.notImplemented(),
* methodNotAllowed: () => new Boom.methodNotAllowed()
* }));
* ```
*
* @param {Object=} options
* @param {Boolean=} options.throw throw error instead of setting status and header
* @param {Function=} options.notImplemented throw the returned value in place of the default NotImplemented error
* @param {Function=} options.methodNotAllowed throw the returned value in place of the default MethodNotAllowed error
* @returns {Function}
*/
Router.prototype.allowedMethods = function (options) {
options = options || {};
var implemented = this.methods;
return function allowedMethods(ctx, next) {
// 所有中间件执行完之后执行allowedMethod方法
return next().then(function() {
var allowed = {};
// 没有响应状态码或者响应了404
if (!ctx.status || ctx.status === 404) {
// 在match方法中,匹配的路由的layer实例对象组成的数组
ctx.matched.forEach(function (route) {
route.methods.forEach(function (method) {
// 把匹配的路由的http方法保存起来,认为是允许的http请求方法
allowed[method] = method;
});
});
var allowedArr = Object.keys(allowed);
// 如果该方法在router实例的methods中不存在
if (!~implemented.indexOf(ctx.method)) {
// 如果在初始化router时配置了throw属性为true
if (options.throw) {
var notImplementedThrowable;
if (typeof options.notImplemented === 'function') {
// 指定了报错函数
notImplementedThrowable = options.notImplemented(); // set whatever the user returns from their function
} else {
// 没有指定则抛出http异常
notImplementedThrowable = new HttpError.NotImplemented();
}
throw notImplementedThrowable;
} else {
// 没有配置throw则响应501
ctx.status = 501;
// 设置响应头中的allow字段,返回允许的http方法
ctx.set('Allow', allowedArr.join(', '));
}
} else if (allowedArr.length) {
if (ctx.method === 'OPTIONS') {
// 如果是OPTIONS请求,则认为是请求成功,响应200,并根据OPTIONS请求约定返回允许的http方法
ctx.status = 200;
ctx.body = '';
ctx.set('Allow', allowedArr.join(', '));
} else if (!allowed[ctx.method]) {
// 如果请求方法在router实例的methods中存在,但是在匹配的路由中该http方法不存在
if (options.throw) {
var notAllowedThrowable;
if (typeof options.methodNotAllowed === 'function') {
notAllowedThrowable = options.methodNotAllowed(); // set whatever the user returns from their function
} else {
notAllowedThrowable = new HttpError.MethodNotAllowed();
}
throw notAllowedThrowable;
} else {
// 响应405 http请求方法错误
ctx.status = 405;
ctx.set('Allow', allowedArr.join(', '));
}
}
}
}
});
};
};Router.prototype.use
/**
* Use given middleware.
*
* Middleware run in the order they are defined by `.use()`. They are invoked
* sequentially, requests start at the first middleware and work their way
* "down" the middleware stack.
*
* @example
*
* ```javascript
* // session middleware will run before authorize
* router
* .use(session())
* .use(authorize());
*
* // use middleware only with given path
* router.use('/users', userAuth());
*
* // or with an array of paths
* router.use(['/users', '/admin'], userAuth());
*
* app.use(router.routes());
* ```
*
* @param {String=} path
* @param {Function} middleware
* @param {Function=} ...
* @returns {Router}
*/
Router.prototype.use = function () {
var router = this;
var middleware = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
var path;
// support array of paths
// 如果第一个参数是一个数组,且数组中元素为字符串
if (Array.isArray(middleware[0]) && typeof middleware[0][0] === 'string') {
// 递归调用use方法
middleware[0].forEach(function (p) {
router.use.apply(router, [p].concat(middleware.slice(1)));
});
return this;
}
var hasPath = typeof middleware[0] === 'string';
if (hasPath) {
path = middleware.shift();
}
middleware.forEach(function (m) {
// 如果这个中间件是由router.routes()方法返回的dispatch中间件,即这是一个嵌套的路由
if (m.router) {
// 遍历router.stack属性中所有的layer
m.router.stack.forEach(function (nestedLayer) {
// 被嵌套的路由需要以父路由path为前缀
if (path) nestedLayer.setPrefix(path);
// 如果父路由有指定前缀,被嵌套的路由需要把这个前缀再加上
if (router.opts.prefix) nestedLayer.setPrefix(router.opts.prefix);
router.stack.push(nestedLayer);
});
if (router.params) {
Object.keys(router.params).forEach(function (key) {
m.router.param(key, router.params[key]);
});
}
} else {
router.register(path || '(.*)', [], m, { end: false, ignoreCaptures: !hasPath });
}
});
return this;
};以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。