本文实例讲述了python条件变量之生产者与消费者操作。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
互斥锁是最简单的线程同步机制,面对复杂线程同步问题,Python还提供了Condition对象。Condition被称为条件变量,除了提供与Lock类似的acquire和release方法外,还提供了wait和notify方法。线程首先acquire一个条件变量,然后判断一些条件。如果条件不满足则wait;如果条件满足,进行一些处理改变条件后,通过notify方法通知其他线程,其他处于wait状态的线程接到通知后会重新判断条件。不断的重复这一过程,从而解决复杂的同步问题。
可以认为Condition对象维护了一个锁(Lock/RLock)和一个waiting池。线程通过acquire获得Condition对象,当调用wait方法时,线程会释放Condition内部的锁并进入blocked状态,(但实际上不会block当前线程)同时在waiting池中记录这个线程。当调用notify方法时,Condition对象会从waiting池中挑选一个线程,通知其调用acquire方法尝试取到锁。
Condition对象的构造函数可以接受一个Lock/RLock对象作为参数,如果没有指定,则Condition对象会在内部自行创建一个RLock。
线程同步经典问题----生产者与消费者问题可以使用条件变量轻松解决。
import threading
import time
class Producer(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
def run(self):
global count
while True:
con.acquire()
if count <20:
count += 1
print self.name," Producer product 1,current is %d" %(count)
con.notify()
else:
print self.name,"Producer say box is full"
con.wait()
con.release()
time.sleep(1)
class Consumer(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
def run(self):
global count
while True:
con.acquire()
if count>4:
count -=4
print self.name,"Consumer consume 4,current is %d" %(count)
con.notify()
else:
con.wait()
print self.name," Consumer say box is empty"
con.release()
time.sleep(1)
count = 0
con = threading.Condition()
def test():
for i in range(1):
a = Consumer()
a.start()
for i in range(1):
b =Producer()
b.start()
if __name__=='__main__':
test()
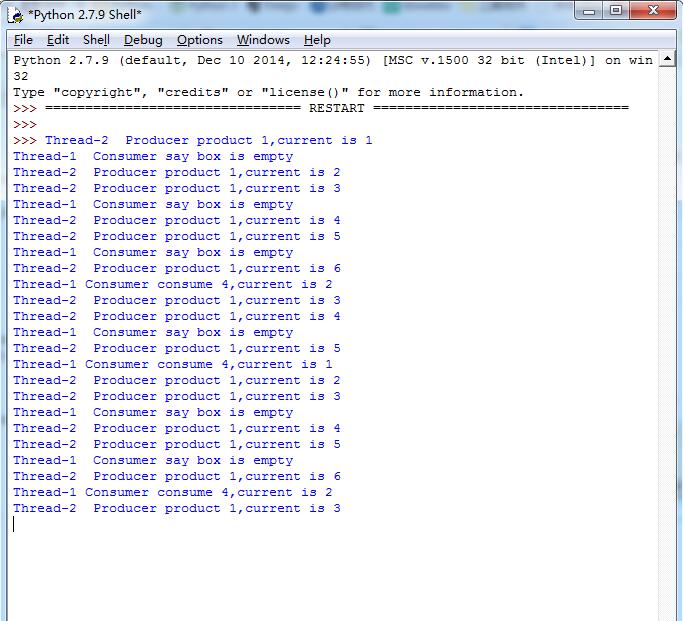
上面的代码假定消费者消费的比较快,输出结果为: