1. 引言
在某些场景下,我们不仅需要进行实时人脸检测追踪,还要进行再加工;这里进行摄像头实时人脸检测,并对于实时检测的人脸进行初步提取;
单个/多个人脸检测,并依次在摄像头窗口,实时平铺显示检测到的人脸;

图 1 动态实时检测效果图
检测到的人脸矩形图像,会依次平铺显示在摄像头的左上方;
当多个人脸时候,也能够依次铺开显示;
左上角窗口的大小会根据捕获到的人脸大小实时变化;

图 2 单个/多个人脸情况下摄像头识别显示结果
2. 代码实现
主要分为三个部分:
摄像头调用,利用 OpenCv 里面的cv2.VideoCapture();
人脸检测,这里利用开源的 Dlib 框架,Dlib 中人脸检测具体可以参考Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 进行人脸检测;
图像填充,剪切部分可以参考Python 3 利用 Dlib 实现人脸检测和剪切;
2.1 摄像头调用
Python 中利用 OpenCv 调用摄像头的一个例子how_to_use_camera.py:
# OpenCv 调用摄像头
# 默认调用笔记本摄像头
# Author: coneypo
# Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie
# GitHub: https://github.com/coneypo/Dlib_face_cut
# Mail: coneypo@foxmail.com
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# cap.set(propId, value)
# 设置视频参数: propId - 设置的视频参数, value - 设置的参数值
cap.set(3, 480)
# cap.isOpened() 返回 true/false, 检查摄像头初始化是否成功
print(cap.isOpened())
# cap.read()
"""
返回两个值
先返回一个布尔值, 如果视频读取正确, 则为 True, 如果错误, 则为 False;
也可用来判断是否到视频末尾;
再返回一个值, 为每一帧的图像, 该值是一个三维矩阵;
通用接收方法为:
ret,frame = cap.read();
ret: 布尔值;
frame: 图像的三维矩阵;
这样 ret 存储布尔值, frame 存储图像;
若使用一个变量来接收两个值, 如:
frame = cap.read()
则 frame 为一个元组, 原来使用 frame 处需更改为 frame[1]
"""
while cap.isOpened():
ret_flag, img_camera = cap.read()
cv2.imshow("camera", img_camera)
# 每帧数据延时 1ms, 延时为0, 读取的是静态帧
k = cv2.waitKey(1)
# 按下 's' 保存截图
if k == ord('s'):
cv2.imwrite("test.jpg", img_camera)
# 按下 'q' 退出
if k == ord('q'):
break
# 释放所有摄像头
cap.release()
# 删除建立的所有窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()2.2 人脸检测
利用 Dlib 正向人脸检测器,dlib.get_frontal_face_detector();
对于本地人脸图像文件,一个利用 Dlib 进行人脸检测的例子:
face_detector_v2_use_opencv.py:
# created at 2017-11-27
# updated at 2018-09-06
# Author: coneypo
# Dlib: http://dlib.net/
# Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie/
# Github: https://github.com/coneypo/Dlib_examples
# create object of OpenCv
# use OpenCv to read and show images
import dlib
import cv2
# 使用 Dlib 的正面人脸检测器 frontal_face_detector
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 图片所在路径
# read image
img = cv2.imread("imgs/faces_2.jpeg")
# 使用 detector 检测器来检测图像中的人脸
# use detector of Dlib to detector faces
faces = detector(img, 1)
print("人脸数 / Faces in all: ", len(faces))
# Traversal every face
for i, d in enumerate(faces):
print("第", i+1, "个人脸的矩形框坐标:",
"left:", d.left(), "right:", d.right(), "top:", d.top(), "bottom:", d.bottom())
cv2.rectangle(img, tuple([d.left(), d.top()]), tuple([d.right(), d.bottom()]), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.namedWindow("img", 2)
cv2.imshow("img", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
图 3 参数 d.top(), d.right(), d.left(), d.bottom() 位置坐标说明
2.3 图像裁剪
如果想访问图像的某点像素,对于 opencv 对象可以利用索引 img [height] [width]:
存储像素其实是一个三维数组,先高度 height,然后宽度 width;
返回的是一个颜色数组(0-255,0-255,0-255),按照(B,G,R)的顺序;
比如蓝色就是(255,0,0),红色是(0,0,255);
所以要做的就是对于检测到的人脸,要依次平铺填充到摄像头显示的实时帧 img_rd 中;
所以进行图像裁剪填充这块的代码如下(注意要防止截切平铺的图像不能超出 640x480 ):
# 检测到人脸
if len(faces) != 0:
# 记录每次开始写入人脸像素的宽度位置
faces_start_width = 0
for face in faces:
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img_rd, tuple([face.left(), face.top()]), tuple([face.right(), face.bottom()]),
(0, 255, 255), 2)
height = face.bottom() - face.top()
width = face.right() - face.left()
### 进行人脸裁减 ###
# 如果没有超出摄像头边界
if (face.bottom() < 480) and (face.right() < 640) and \
((face.top() + height) < 480) and ((face.left() + width) < 640):
# 填充
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
img_rd[i][faces_start_width + j] = \
img_rd[face.top() + i][face.left() + j]
# 更新 faces_start_width 的坐标
faces_start_width += width记得要更新faces_start_width的坐标,达到依次平铺的效果:
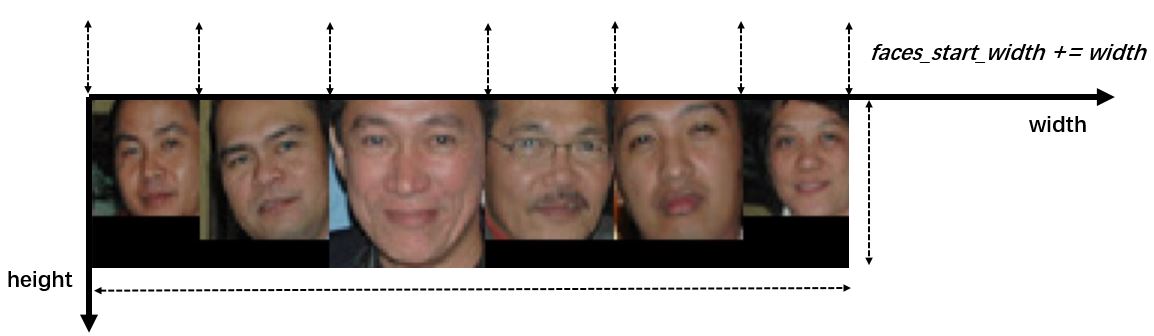
图 4 平铺显示的人脸
2.4. 完整源码
faces_from_camera.py:
# 调用摄像头实时单个/多个人脸检测,并依次在摄像头窗口,实时平铺显示检测到的人脸;
# Author: coneypo
# Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie
# GitHub: https://github.com/coneypo/Dlib_face_cut
import dlib
import cv2
import time
# 储存截图的目录
path_screenshots = "data/images/screenshots/"
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('data/dlib/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 创建 cv2 摄像头对象
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 设置视频参数,propId 设置的视频参数,value 设置的参数值
cap.set(3, 960)
# 截图 screenshots 的计数器
ss_cnt = 0
while cap.isOpened():
flag, img_rd = cap.read()
# 每帧数据延时 1ms,延时为 0 读取的是静态帧
k = cv2.waitKey(1)
# 取灰度
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# 人脸数
faces = detector(img_gray, 0)
# 待会要写的字体
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
# 按下 'q' 键退出
if k == ord('q'):
break
else:
# 检测到人脸
if len(faces) != 0:
# 记录每次开始写入人脸像素的宽度位置
faces_start_width = 0
for face in faces:
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img_rd, tuple([face.left(), face.top()]), tuple([face.right(), face.bottom()]),
(0, 255, 255), 2)
height = face.bottom() - face.top()
width = face.right() - face.left()
### 进行人脸裁减 ###
# 如果没有超出摄像头边界
if (face.bottom() < 480) and (face.right() < 640) and \
((face.top() + height) < 480) and ((face.left() + width) < 640):
# 填充
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
img_rd[i][faces_start_width + j] = \
img_rd[face.top() + i][face.left() + j]
# 更新 faces_start_width 的坐标
faces_start_width += width
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Faces in all: " + str(len(faces)), (20, 350), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
# 没有检测到人脸
cv2.putText(img_rd, "no face", (20, 350), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# 添加说明
img_rd = cv2.putText(img_rd, "Press 'S': Screen shot", (20, 400), font, 0.8, (255, 255, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
img_rd = cv2.putText(img_rd, "Press 'Q': Quit", (20, 450), font, 0.8, (255, 255, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# 按下 's' 键保存
if k == ord('s'):
ss_cnt += 1
print(path_screenshots + "screenshot" + "_" + str(ss_cnt) + "_" + time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S",
time.localtime()) + ".jpg")
cv2.imwrite(path_screenshots + "screenshot" + "_" + str(ss_cnt) + "_" + time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S",
time.localtime()) + ".jpg",
img_rd)
cv2.namedWindow("camera", 1)
cv2.imshow("camera", img_rd)
# 释放摄像头
cap.release()
# 删除建立的窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()这个代码就是把之前做的人脸检测,图像拼接几个结合起来,代码量也很少,只有100行,如有问题可以参考之前博客:
Python 3 利用 Dlib 进行人脸检测
Python 3 利用 Dlib 实现人脸检测和剪切
人脸检测对于机器性能占用不高,但是如果要进行实时的图像裁剪拼接,计算量可能比较大,所以可能会出现卡顿;
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。